Many patients prefer PGT because it offers a proactive approach to family planning. By screening embryos for genetic abnormalities, prospective parents can make informed decisions, reducing the likelihood of passing on hereditary diseases. This proactive stance contributes to a higher chance of having healthy pregnancies and, ultimately, healthy children.
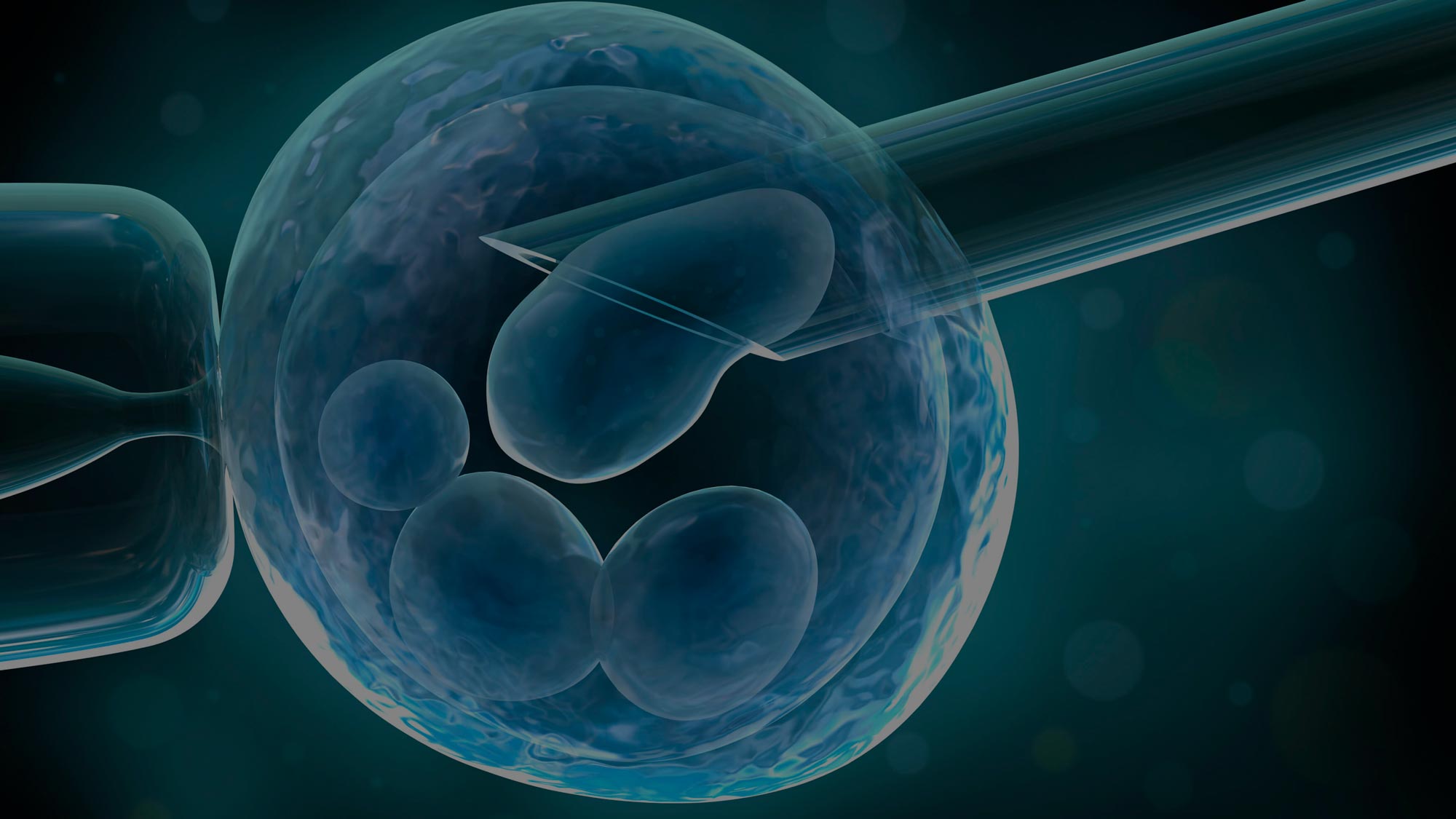
Preimplantation Genetic Testing
PGD/PGS
When the parent(s) are carriers of a genetic condition (unbalanced chromosomal rearrangement or gene mutation), a genetic diagnostic (PGD) can help to determine whether that condition has been transmitted to the embryos.
What is PGT?
PGT- Preimplantation genetic testingdetects and prevents the transmission to offspring of severe hereditary diseases caused by genetic and chromosomal abnormalities of embryos before they are transferred to the uterus. It also prevents the transfer of embryos that cannot lead to pregnancy.


Preimplatation Genetic Screening (PGS)
Even if the parents have no known genetic abnormalities, their embryos can also be screened for chromosomal abnormalities to determine if the embryo has too many or too few chromosomes.
DON'T MISS YOUR CHANCE TO BECOME HAPPIER!
Surrogacy with Vita Nova
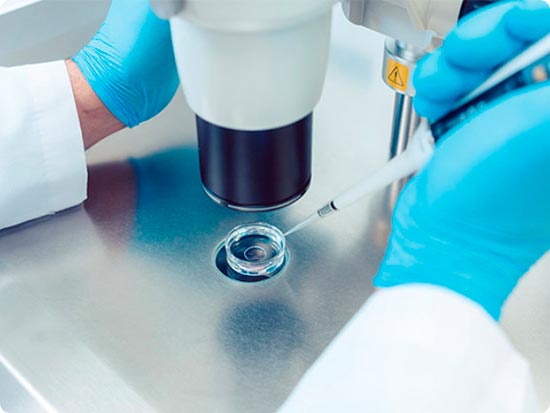
How does PGT work?
Preimplantation genetic testing is a test that is performed after the completion of IVF, when the eggs are fertilized and the embryos begin to divide.
A genetic test can be performed as soon as the embryo has reached the 8-cell stage (approximately on the 3rd day of development), by removing one cell (blastomere biopsy). Then the embryo returns to the incubator for further growth.
However, it is recommended to perform a biopsy as soon as the embryos turn into blastocysts (day 5-6). By the 5th day of development, the embryos will divide into about 100 cells and form the outer layer, which will eventually become the placenta. At this stage, a trophoblast biopsy can be performed by removing several cells from the outer layer. This procedure does not affect the quality of the embryo or its ability to implant.

